
The end result is that not only has AMD built their biggest GPU ever, but they have done virtually everything they can to maximize the amount of die space they get to allocate to FP32 and rendering resources.

4096-bits of HBM PHYs still takes up a fair bit of space – though AMD won’t tell us how much – but it’s notably lower than the amount of space AMD was losing to Hawaii’s GDDR5 memory controllers. This is in part due to the fact that HBM stacks have their own logic layer, distributing some of the logic on to each stack, and furthermore a benefit of the fact that the signaling logic that remains doesn’t have to be nearly as complex since the frequencies are so much lower. Along with HBM’s bandwidth and power benefits, HBM is also much simpler to implement, requiring less GPU space for PHYs than GDDR5 does. Fiji will not be a FP64 powerhouse – its 4GB of VRAM is already perhaps too large of a handicap for the HPC market – so instead we get AMD’s best FP32 GPU going against NVIDIA’s best FP32 GPU.ĪMD’s final ace up their sleeve on die size is HBM. This is a significant departure from Hawaii, which implemented native support for ½ rate, and on consumer parts offered a handicapped 1/8 rate.
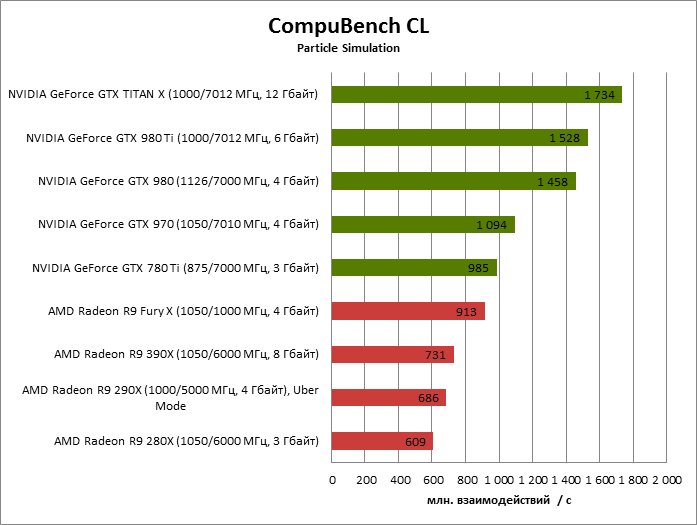
With GCN supporting power-of-two FP64 rates between 1/2 and 1/16, AMD has gone for the bare minimum in FP64 performance that their architecture allows, leading to a 1/16 FP64 rate on Fiji.

Along with producing the biggest die they could, AMD has also more or less gone the direction of NVIDIA and Maxwell in the case of Fiji, building what is unambiguously the most gaming/FP32-centric GPU the company could build. The fact that Fiji comes at the latter-half of the 28nm process’s life time means that such a large GPU is not nearly as risky now as it would have been in 2011/2012 (NVIDIA surely took some licks internally on GK110), but still, nothing else we can show you today can really sell the significance of Fiji to AMD as much as the die size can.Īnd the fun doesn’t stop there. And yet Fiji dwarfs it, coming in at 158mm2 (36%) larger. When Hawaii was released in 2013 at 438mm2, it was already AMD’s biggest GPU ever for its time. Looking at Fiji relative to AMD’s other big GPUs, it becomes very clear very quickly just how significant this change is for AMD. TSMC can’t build chips any bigger than this Fiji is as big a chip as AMD can order. Fiji’s 596mm2 die size is just 5mm2 (<1%) smaller than NVIDIA’s GM200, and more notably still hits TSMC’s 28nm reticle limit. The end result is that for the first time since the unified shader era began, AMD has gone toe-to-toe with NVIDIA on die size. Altogether they’re riskier than smaller chips, and while there are times where they are necessary, AMD has never reached this point until now. Big chips are expensive to develop, expensive to produce, take longer to develop, and yield worse than small chips (this being especially the case early-on for 40nm). As we mentioned in our introduction, AMD has traditionally shied away from big chips, even after the “small die” era ended, and for good reason. More than anything else, it’s simply huge, 596mm2 to be precise. We’ll get to HBM in detail in a bit, but it’s important to call out the impact of HBM and the interposer early, since they have a distinct impact on how Fiji was designed and what its capabilities are.Īs for Fiji itself, Fiji is unlike any GPU built before by AMD, and not only due to the use of HBM. Essentially a very large chip without any expensive logic on it, the silicon interposer allows for finer, denser signal routing than organic packaging is capable of, making the ultra-wide 4096-bit HBM bus viable for the first time. The job of the interposer is to sit between the package and the GPU, serving as the layer that connects the on-package HBM memory stacks with the GPU. Whereas past GPUs were defined by the GPU die itself and then the organic substrate package it sits on, the inclusion of HBM requires a third layer, the silicon interposer.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
